Understanding Foundation Model - Part 2 (Attention is All you need)
A high level overview of how transformer architecture works
GPT stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer. The term transformer is associated with ChatGPT, Claude, LLaMA because all of these model use transformer architecture. So what is it?
Suppose you're reading a paragraph:
“The ball couldn’t go through the door because it was too wide.”
You instantly know “it” refers to the ball and not the suitcase because your brain considers the context of every word. Human brain don’t just process words one after another. You look at the whole sentence together, break it and sometimes even refer the previous sentence to understand the meaning.
This way of looking at information is what Transformer architecture brings to AI. This is called attention mechanism and it is what gives models like ChatGPT, Claude, and LLaMA their power. It’s how they decide which parts of the input to focus on when generating an output.
In traditional models, the system reads inputs one word at a time with no ability to look back. But attention allows the model to weigh the importance of each word relative to every other word.
Let’s understand with an example:
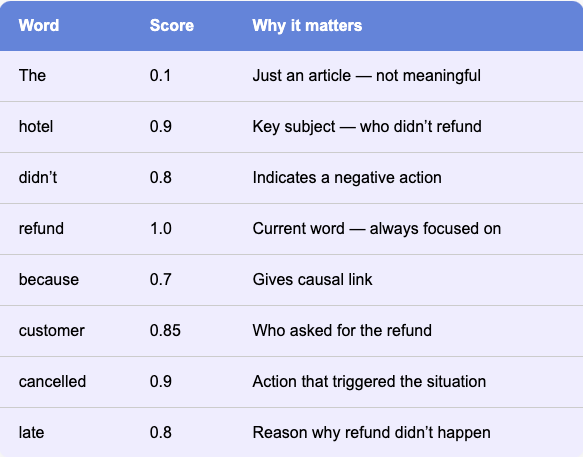
“The hotel didn’t refund because the customer cancelled late.”
When the model processes the word “refund,” it must understand:
Who did the refund? → hotel
Why did it happen? → because
Who was involved? → customer
What action triggered it? → cancelled
In simple terms, the attention mechanism assigns a score to each word in the input to decide which ones matter most when predicting the next word.
As a product manager not managing a LLM product it might not be necessary to understand the math behind it but the concept overview.
When the model is at the word “refund”, it:
Looks at every word in the sentence — from “The” to “late”
Assigns a score to each one based on how relevant it is to “refund”
Focuses more on words with higher scores
The model uses these scores to pay closer attention to the important words like hotel, customer, cancelled, and late with higher score while mostly ignoring less relevant ones like The or amount. This helps it make sense of what refund really means in this context: who was involved, what happened, and why the refund was denied. The model can then predict what should come next like “due to policy” or “could not be processed.”
The Transformer architecture didn’t just advance AI, it redefined what machines could do with language. And if you're working anywhere near AI, it’s worth learning how it works. You don’t have to know the math. But you do need to know what’s happening under the hood because that’s where product decisions begin.
Reference:
The Transformer architecture was introduced in the landmark 2017 paper “Attention Is All You Need” by Vaswani et al., which laid the foundation for modern large language models.